Menu

Air Volume for Kitchens
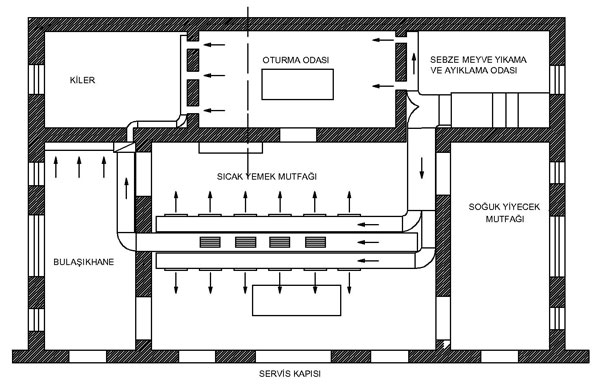
Fresh and exhaust air volume required for the ventilation of kitchens is expressed as m3/h.
The flow rates of ventilating air defined as mentioned above are indicated in Table 14.56. Air change rate in the environment could be calculated by means of said values. If air quantity read from the table is 60 m3/h and the room is 3 m in height, then air will be changed 60/3=20 times per hour. The more sensitive and precise method to determine the air flow rate is the calculation made in terms of number, type and size of kitchen equipment. Required amount of air is shown in Table 14.57 according to the type and size of devices.
A diversity factor should be considered for the calculation of total air amount. The said diversity factor ranges between 0,5 - 0,8 for big kitchens and 0,8 - 1 for small kitchens. Fresh air was being captured less than the exhaust air in order to build up low pressure in the past years. However, equal amount of air is recommended for today's applications. Therefore neutral pressure will occur in kitchen areas.
Low pressure is applied only for small kitchens. Also, much more fresh air is supplied at critical areas in terms of hygiene (cold kitchen, meat preparation etc.) It will be balanced in other areas. When charged in small quantities, the flow rate can be reduced by means of speed control switch in extraction fan and aspirator. Allowable noise level is between 50-60 dßA for the kitchen areas.
When local ventilating air that is required to be extracted by kitchen hood is much more than the necessary fresh air amount of kitchen, heat-saving kitchen hoods are used. As may be seen from the Figure 14.58, fresh air corresponding to 20-30% of air that is required to be exhausted from kitchen is supplied by central ventilation unit in a way that is conditioned. The said air is conditioned in a way that meets the heating (or cooling) requirement of the ambient air.
Table 14.56 - CLEAN AIR RATES FOR 1 m2 AREA IN m3/h
Table 14.57 - LATENT AND SENSIBLE HEAT GAINS FROM KITCHEN DEVICES, VAPOR EMISSION AND AIR QUANTITY THAT WILL COMPENSATE THESE CHARGES WITH ?t = 8K TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE OR ?x = 5 g/kg SPECIFIC HUMIDITY DIFFERENCE
The remaining conditioned fresh air at the rate of 70-80% is vented to kitchen hood by special supply fan. The air blown to the filters fitted to exhaust vents of kitchen hoods from the sides of hood in a jet form and the air extracted from the room at the rate of 20-30% is discharged to the atmosphere with exhaust fan.
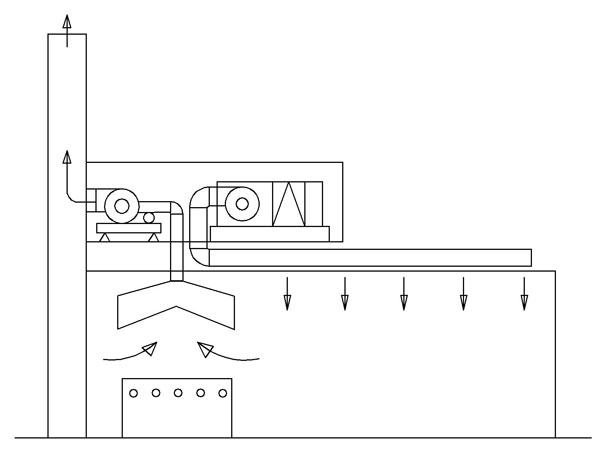
Polluted air above the stove, oven or another source is vented towards to kitchen hood efficiently with the help of induction effect generated by air jet blown from side parts. Such devices ensure great energy-saving because whole of the ventilation air is not heated and cooled down.
Another type of these devices is shown in Figure 14.59. It is an independent system specially designed for kitchen. Fresh air extracted by supply air is separated into two parts. Air conditioning requirement of the room is met by heating the required amount of air between 20-100% in winter time and cooling down in summer time. Remaining part that equals to 80-0% is vented into the kitchen hood without being conditioned.
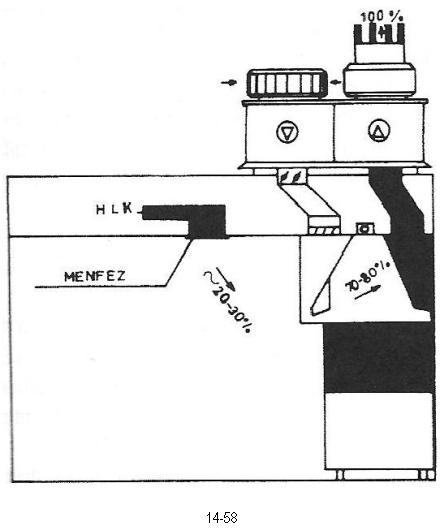
Figure 14.58 HEAT-SAVING KITCHEN HOOD
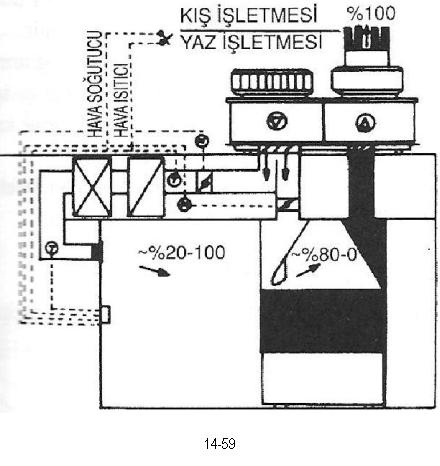
Figure 14.59 DIFFERENT TYPE HEAT-SAVING KITCHEN HOOD
This system features free-cooling. When antalpic sensor detects that outdoor air is colder than indoor air during summer time, all system will be run by using outdoor air. That means that the whole of fresh incoming air is blown into the room. Thus, it is possible to cool the indoor air without consuming energy at nights and intermediate seasons.
Source of pictures and articles: Studies of Isisan Academy no:305
Air conditioning manual, updated 3rd edition